[Spring Security] Spring Security FilterChain 동작 원리 완전 해부
[Spring Security] Spring Security FilterChain 동작 원리 완전 해부
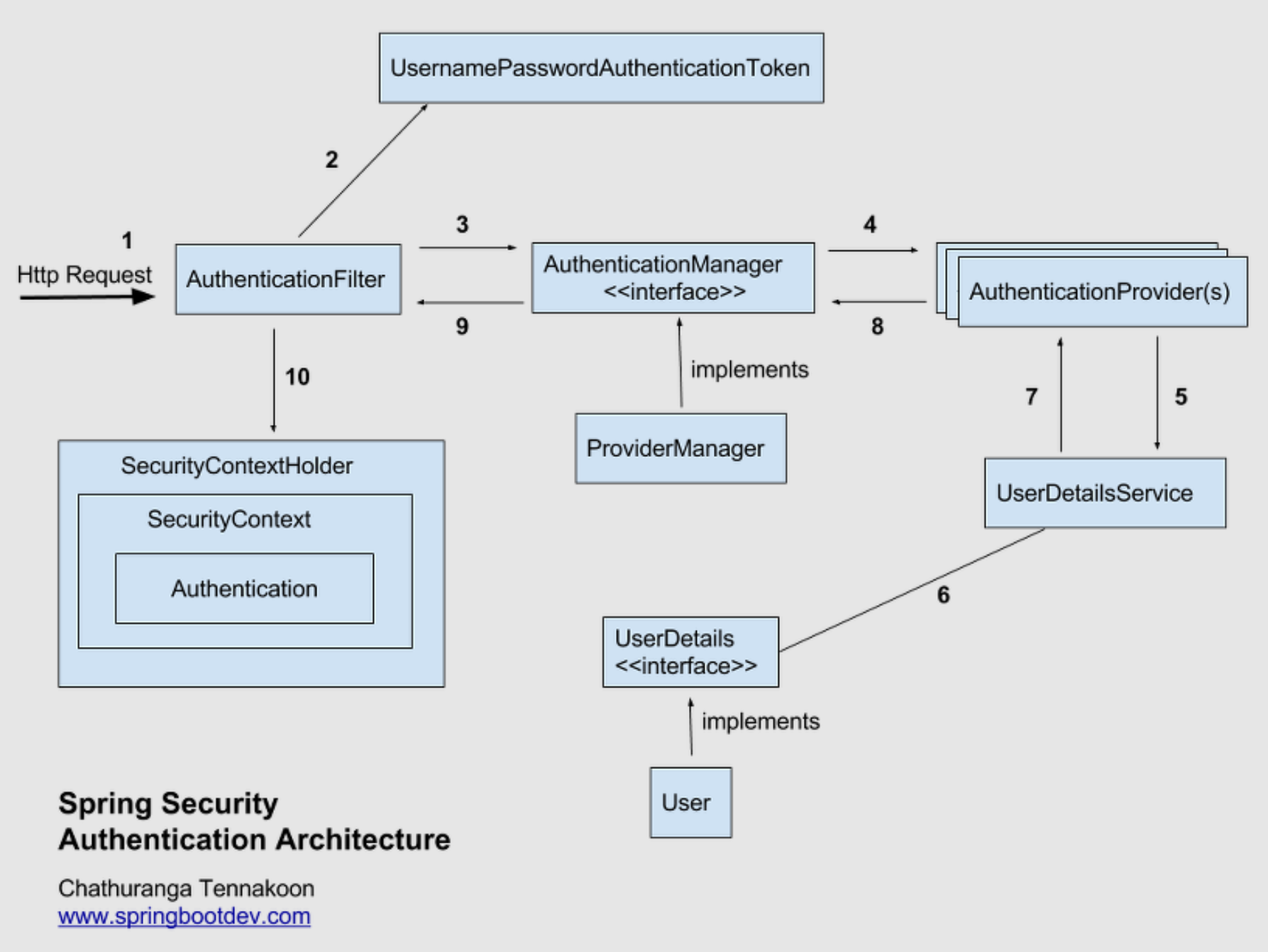
1. Security Filter1. Security Filter 개요1. Security Filter 주요 역할일련의 서블릿 필터 체인을 자동으로 구성한다.일반적으로 웹 환경에서 브라우저가 서버에 요청을 보내게 되면 DispatcherServlet이 요청 받
crushed-taro.tistory.com
1. Security Filter
1. Security Filter 개요
1. Security Filter 주요 역할
- DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
- FormLogin() 메서드 호출 시 양식을 기반으로 인증을 활성화하는 필터로 로그인된 사용자의 url에 사용자 이름과 암호를 제출하는 로그인 양식으로 기본 로그인 페이지를 생성하게 되며 실패한 로그인 시도에 대한 사용자 정의할 수 있는 오류 메시지를 포함하는 기능을 제공하고 있다.
- 로그인 요청 시 기본 로그인 페이지 생성을 담당하는 필터이다.
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin().loginPage("/auth/login") // 해당 요청시 로그인 페이지로 이동됨
.defaultSuccessUrl("/") // 로그인 성공시 해당 페이지로 이동함
.failureUrl("/") // 로그인 실패시 해당 페이지로 이동됨
}
- BasicAuthenticationFilter
- 기본 인증을 처리하는 Spring security에서 제공하는 필터로 기본 인증은 사용자 자격 증명(사용자 이름 및 암호)이 인코딩되어 각 요청에 HTTP 헤더로 전송되는 간단한 인증 메커니즘이다.
- 인증이 필요한 요청을 가로채고 기본 인증 체계로 Authorization 헤더가 있는지 확인하여 헤더가 있는 경우 필터는 인코딩된 자격 증명을 추출하여 사용자 인증을 시도한다.해당 필터는 base 64 인코딩 형식으로 자격 증명을 전송하기 때문에 HTTPS를 사용한 양식 기반 인증을 하는 것이 더욱 안전하다.
- 실제 인증은 AuthenticationProvider에서 담당하며 AuthenticationManger에서 구성이 되어 있다. 이러한 방식으로 BasicAuthenticationFilter를 구성하게 되면 SpringSecurity는 요청이 있을 때 Authorization 헤더에서 인코딩된 자격 증명을 추출하여 사용자 인증을 시도할 때 기본 인증 프로세스를 처리하게 된다.
- 해당 필터는 base 64 인코딩 형식으로 자격 증명을 전송하기 때문에 HTTPS를 사용한 양식 기반 인증을 하는 것이 더욱 안전하다.
public class BasicAuthenticationCustomFilter extends BasicAuthenticationFilter{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new BasicAuthenticationCustomFilter()) // 필터 커스텀
- RememberMeAuthenticationFilter
- 세션이 만료된 사용자에게 Remember-me 토큰을 기반으로 사용자를 자동으로 인증할 수 있도록 한다.
- 해당 필터를 구현하게 되면 RememberMeServices를 상속받아 구현해야 하며 토큰 유효성 검사 및 인증 설정을 해주어야 한다. PersistentTokenBasedRememberMeServices 구현이 사용되며 UserDetailService 구현이 필요하다.
- 해당 필터는 적절한 보안 조치가 필요하며 토큰은 애플리케이션의 보안을 보장하기 위해 안정하게 저장되고 적절하게 검증되어야 한다.
public class RememberMeAuthenticationCustomFilter extends RememberMeAuthenticationFilter {
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new RememberMeAuthenticationCustomFilter ()) // 필터 커스텀
- SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
- HttpServletRequest 에 액세스하는 컨트롤러 또는 기타 필터와 같은 후속 구성 요소에서 보안 컨텍스트를 사용할 수 있으며 해당 구성 요소가 보안 컨텍스트에서 현재 사용자의 인증 및 권한 부여 정보를 검색할 수 있다.
- 애플리케이션이 활성화 되어 있을 때 Security에 의해 자동으로 추가된다.
- HttpServletRequest 에 SecurityContextHolder를 설정하는 필터로 현재 보안 컨텍스트를 인식하도록 보장하는 Spring Security에서 제공하는 필터이다. 텍스트를 인식하도록 보장하는 Spring Security 에서 제공하는 필터로 사용자 요청에 대한 보안 컨텍스트를 설정하여 후속 처리 구성 요소가 보안 정보에 액세스할 수 있도록 한다.
public class SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestCustomFilter extends SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestCustomFilter()) // 필터 커스텀
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- 익명 사용자에게 인증을 요구하지 않고 애플리케이션에 특정 부분을 액세스할 수 있도록 하는 filter이다.
- 익명 사용자의 인증 정보를 관리하는 객체는 AnonymousAuthenticationToke 구성되어 있으며 기본 설정으로 이름은 anonymous User 권한 및 역할로 Granted Authority 목록을 생성하여 ROLE_ANONYMOUS로 익명 사용자에게 할당된다.
- 인증 객체를 생성하여 다른 인증이 설정되지 않으면 SecurityContextHolder 에 설정하는 역할을 하게 된다.
public class AnonymousAuthenticationCustomFilter extends AnonymousAuthenticationFilter{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new AnonymousAuthenticationCustomFilter ()) // 필터 커스텀
- sessionManagementFilter
- 사용자의 요청에 따라 세션을 효과적으로 관리하기 위해서 사용하는 필터이다.
- 사용자의 세션을 관리하는 필터로 새로운 세션을 생성하거나 무효화, 고정 세션 공격 보호 등 세션의 동시성 제어를 포함한 세션 정책을 시행하게 된다.
public class sessionManagementCustomFilter extends sessionManagementFilter{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new sessionManagementCustomFilter()) // 필터 커스텀
http..sessionManagement() // 세션 설정을 해주겠다는 메소드
.maximumSessions(1) // 동일 세션으로 1명의 사용자만 로그인 허용
.expiredUrl("/") // 이미 로그인이 되어 세션 생성에 제한이 되었을 경우 리다이렉트 할 주소
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false); // boolean 값으로 false : 이전 사용자의 강제 로그아웃 true : 신규 사용자의 로그인 실패
- ExceptionTranslationFilter
- 액세스가 거부될 때 인증 프로세스를 시작하는 역할을 하는 AuthenticatiojnEntryPoint의 인스턴스로 구성되어 있다. 인증 및 권한 부여 관련 예외를 포착하여 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉션을 하거나 오류를 반환하는 것과 같은 응답을 트리거하도록 되어 있다.
- 인증 및 권한 부여 프로세스 중에 발생하는 예외를 포착하여 이를 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉션 처리하거나 오류 응답을 반환하는 것과 같은 적절한 변환을 하는 역할을 하게 된다.
public class ExceptionTranslationCustomFilter extends ExceptionTranslationFilter{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new ExceptionTranslationCustomFilter()) // 필터 커스텀
http.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedPage("/access-denied") // Exception 발생시 이동할 페이지
- FilterSecurityInterceptor
- 보안 규칙을 기반으로 액세스 제어를 수행하는 SpringSecurity에서 제공하는 키 필터이다. 권한 부여 규칙을 적용하고 사용자가 특정 리소스에 액세스하거나 특정 작업을 수행할 수 있는지를 결정하게 된다. FilterSecurityInterceptor는 SpringSerucity 필터 체인에 있으며 보호된 리소스에 도달하기 전에 요청을 가로채게 된다.
- 정의된 보안 구성에 대한 요청된 url 및 관련 HTTP 메서드를 평가하여 사용자가 진행할 수 있는 권한이 있는지 확인한다.
public class FilterSecurityCustomInterceptor extends FilterSecurityInterceptor{
// 로직 작성
}
http.addFilter(new FilterSecurityCustomInterceptor()) // 필터 커스텀
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public").permitAll() // 해당 요청은 모두가 사용이 가능함
.anyRequest().authenticated()